Mosquito Borne Diseases
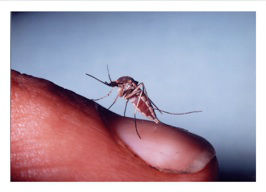
Mosquitoes and Disease – We work together with the State and County health departments to reduce the likelihood of local transmission. The rapid spread of West Nile Virus across North American illustrates that new mosquito-borne diseases can be introduced anywhere, any time. Our comprehensive mosquito surveillance and control program is aimed at predicting and preventing similar disease outbreaks in Northern Salinas Valley and the Monterey Peninsula.
Some species of mosquitoes are involved in the transmission of important disease-causing agents (pathogens). In California, these diseases include encephalitis viruses, malaria and dog heartworm. These pathogens are specifically adapted to transmission by mosquitoes. Most pathogens of humans such as measles, hepatitis or HIV (AIDS) viruses cannot develop in mosquitoes.
West Nile Virus – For up to date WNV activity in California you may visit their website: www.westnile.ca.gov.
Western Equine Encephalomyelitis (WEE), Saint Louis Encephalitis (SLE), and West Nile Virus (WNV) – These viruses transmitted by mosquitoes can cause a serious and potentially fatal inflammation of the brain in horses and humans. Wild birds, serve as a reservoir host. Mosquitoes can pick up the virus by biting infected birds and later transmit it to humans and horses, which are “dead end hosts” (cannot pass the virus on to others). The Northern Salinas Valley Mosquito Abatement District maintains sentinel chicken flocks to serve as an early warning system to these diseases.
ZIKA
Zika virus spreads to people primarily through the bite of an infected Aedes species mosquito (Ae. aegypti and Ae. albopictus). People can also get Zika through sex with an infected man, and the virus can also be passed from a pregnant woman to her unborn child.
